Thread angle
The thread angle of a screw is the included angle between the thread flanks, measured in a plane containing the thread axis.[1] This is a defining factor for the shape of a screw thread. Standard values include:
| Name | Code | Angle | Profile | Standards |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Most V-threads (including ISO, NPT and UTS) | M | 60° |  |
DIN 13 / ISO ? / ASME/ANSI ? |
| Whitworth threads | W | 55° |  |
DIN 49301 / BS ? |
| British standard pipe thread | G | 55° |  |
DIN / BS / EN / ISO 228-1 / ISO 7-1 |
| National Pipe Thread | NPT | 60° |  |
ASME B1.20.-1983 Pipe Threads, General Purpose, Inch |
|
Rd | 30° |  [5] [5] |
DIN 405 / DIN 20400 |
| Acme thread[6] | 29° |  |
ASME/ANSI B1.5-1988[7] | |
| Metric trapezoidal threads[1] | Tr | 30° |  |
DIN 103 |
| Buttress threads[6] | S | 45° |  |
DIN 2781 |
| German buttress threads[6] | S | 30° |  |
DIN 513 |
| Square threads[1] | Sq | 0° |  |
? |
| Panzergewinde, "steel conduit thread" | Pg | 80° |  |
DIN 40430 |
| British Association (BA) thread | BA | 47° 30' = 47.5° | 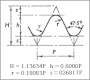 |
BS 93:2008 |
| Löwenherz thread[8] | 53° 8' ≈ 53.1° | |||
| Bodmer thread[9] | 50° |

Diagram of a thread angle
References
Notes
Bibliography
- Bhandari, V B (2007), Design of Machine Elements, Tata McGraw-Hill, ISBN 978-0-07-061141-2.
- Oberg, Erik; Jones, Franklin D.; Horton, Holbrook L.; Ryffel, Henry H. (1996), Green, Robert E.; McCauley, Christopher J. (eds.), Machinery's Handbook (25th ed.), New York: Industrial Press, ISBN 978-0-8311-2575-2, OCLC 473691581.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.