Tobaniviridae
Tobaniviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect vertebrates.[1] Host organisms include mammals, fish, and snakes. The genome size of tobaniviruses ranges from 20 to 32 kilobases.[2] The family is the only member of the suborder Tornidovirineae.[1]
| Tobaniviridae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Electron micrograph of virion and structure of bovine torovirus | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Pisoniviricetes |
| Order: | Nidovirales |
| Suborder: | Tornidovirineae |
| Family: | Tobaniviridae |
| Subfamilies and genera[1] | |
|
See text | |
Taxonomy
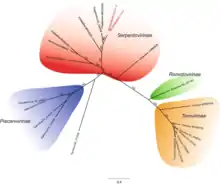
Phylogenetic tree of family Tobaniviridae
The family Tobaniviridae has four subfamilies and eight genera:[1]
- Piscanivirinae
- Bafinivirus
- Oncotshavirus
- Remotovirinae
- Bostovirus
- Serpentovirinae
- Infratovirus
- Pregotovirus
- Sectovirus
- Tiruvirus
- Torovirinae
References
- "Virus Taxonomy: 2018 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). October 2018. Retrieved 27 January 2019.
- Ferron, François; Debat, Humberto J.; Shannon, Ashleigh; Decroly, Etienne; Canard, Bruno (2020-03-01). "A N7-guanine RNA cap methyltransferase signature-sequence as a genetic marker of large genome, non-mammalian Tobaniviridae". NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics. 2 (1): lqz022. doi:10.1093/nargab/lqz022. PMC 7107822. PMID 32289120.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.