Bugkalot language
Bugkalot (also Ilongot) is a language of the indigenous Bugkalot people of northern Luzon, Philippines.
Not to be confused with the Ilongo language, also of the Philippines.
| Bugkalot | |
|---|---|
| Region | Eastern Nueva Vizcaya and Western Quirino, Philippines |
| Ethnicity | Bugkalot |
Native speakers | (51,000 cited 1990 census)[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | ilk |
| Glottolog | ilon1239 |
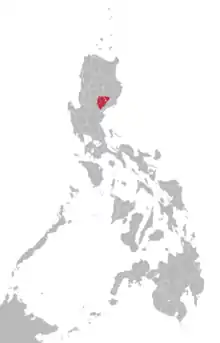 Area where Bugkalot is spoken[1] | |
Distribution
Ethnologue lists the following provinces in which Ilongot is spoken.
- Most of Quirino Province north of the Cagayan River
- Eastern Nueva Vizcaya Province
- Southern Isabela Province (upper reaches of the Cagayan River)
Dialects
Ethnologue lists the following dialects.
- Abaka (Abaca)
- Egongot
- Ibalao (Ibilao)
- Italon
- Iyongut
Alternate names include Bugkalut, Bukalot, and Lingotes.
References
- Bugkalot at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
| Official languages | |
|---|---|
| Regional languages | |
| Indigenous languages (by region) | |
| Immigrant languages | |
| Sign languages | |
| Historical languages | |
| Batanic (Bashiic) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Luzon |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Luzon |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Northern Mindoro | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greater Central Philippine |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kalamian | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bilic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sangiric | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minahasan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other branches |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reconstructed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.